The Greek crisis spread further last week, not only to Portugal and Spain, but in addition to battering global equity markets, contagion spread to bank credit spreads, OIS-libor and emerging market debt. In response, European Union finance ministers have rushed to “shock and awe” the markets by formulating a “crisis mechanism” package with the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The package includes loan guarantees and credits worth as much as EUR 750 billion. The support package can be added to the EUR 110 billion loan package announced last week.
In addition, the US Federal Reserve (Fed) announced the authorisation of temporary currency swaps through January 2011 between the Fed, European Central Bank (ECB), Bank of Canada (BoC), Bank of England (BoE) and Swiss National Bank (SNB) in order to combat in the “the re-emergence of strains” in European markets. Separately, the ECB will conduct sterilised interventions in public and private debt markets, a measure that was hoped would be announced at the ECB meeting last week, but better late than never. The ECB did not however, announce direct measures to support the EUR.
The significance of these measures should not be underestimated and they will go a long way to reducing money market tensions and helping the EUR over the short-term. Indeed, recent history shows us that the swap mechanisms work well. The size of the package also reduced default and restructuring risks for European sovereigns. However, the risk is that it amounts to a “get out of jail free card” for European governments. A pertinent question is whether the “crisis mechanism” will keep the pressure on governments to undertake deficit cutting measures.
The Greek crisis has gone to the heart of the euro project and on its own the package will be insufficient to turn confidence around over the medium term. In order to have a lasting impact on confidence there needs to be proof of budget consolidation and increasing structural reforms. Positive signs that the former is being carried out will help but as seen by rising public opposition in Greece, it will not be without difficulties whilst structural reforms will take much longer to implement. Confidence in the eurozone project has been shattered over recent months and picking up the pieces will not be an easy process.
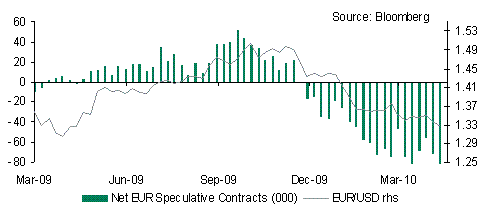
Some calm to markets early in the week will likely see the USD lose ground. There was a huge build up of net USD long positioning over the last week as reflected in the CFTC IMM data, suggesting plenty of scope for profit taking and/or offloading of USD long positions. In contrast, EUR positioning fell substantially to yet another record low. Some short EUR covering is likely in the wake of the new EU package, but EUR/USD 1.2996 will offer tough technical resistance followed by 1.3114.
The EU/IMF aid package will help to provide a strong backstop for EUR/USD but unless the underlying issues that led to the crisis are resolved, EUR/USD is destined to drop further. Perhaps there will be some disappointment for the EUR due to the fact that the package of support measures involves no FX intervention. This could even limit EUR upside given that there was speculation that “defending the EUR” meant physically defending the currency. In the event the move in implied FX volatility over the last week did not warrant this.