The end of last week proved to be a calmer affair than the preceding few days. There was some encouraging news on the Greek front, with Germany finally approving its share of the European Union (EU) aid package whilst Greece appeared to be on track with its budget deficit reduction as the country recorded a cash deficit of EUR 6.3billion in the first four months of the year, a 42% reduction compared to a year earlier. EU officials also agreed on tougher sanctions for countries breaching austerity rules.
There were plenty of negatives to offset the good news however, as European business surveys including the German IFO index and flash eurozone purchasing managers indices (PMIs) revealed some loss of momentum in growth as well as increased divergence. European banking sector concerns intensified as the Bank of Spain was forced to take control of CajaSur, a small savings bank holding 0.6% of total Spanish banking assets, which faced difficulties due to distressed real estate exposure. Its woes highlighted the problems faced by many Spanish savings banks due to property market exposure.
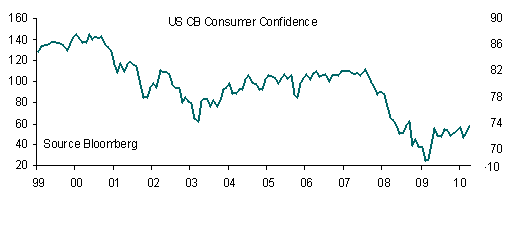
US data releases this week will confirm that economic recovery gathered steam in Q2. May consumer confidence data is likely to record a small gain, due in large part to improving job market conditions, whilst the Chicago PMI is set to retrace slightly in May, albeit from a healthy level. Both new and existing home sales are set to record gains in April, the former following a sizeable gain in March although the drop in house prices likely to be revealed by the Case-Shiller index will continue to fuel doubts about the veracity of the turnaround in the US housing market.
In Europe there is not much in terms of first tier releases and highlights include sentiment data such as German Gfk and French consumer confidence indices, and the May French business confidence indicator. The data are likely to be mixed, and as indicated by last week’s surveys will reflect a relatively healthy Q2 2010, but a worsening outlook for the second half of the year.
In the absence of UK data today there will be plenty of attention on the details of plans by Chancellor Osborne to cut GBP 6 billion from the budget deficit. The measures will be small change ahead of the emergency budget package on June 22nd when much bigger cuts are expected. Nonetheless, the first step today will be a crucial test of the new government’s ability to convince ratings agencies and markets that it is serious about reducing the burgeoning fiscal deficit.
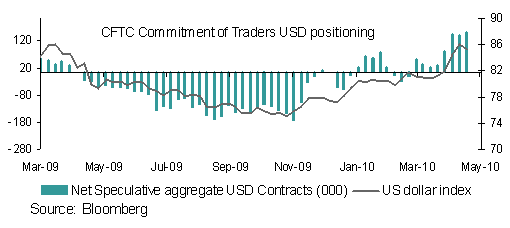
Following the massive positioning adjustments of the last week markets will look somewhat calmer over coming days but risk aversion is likely to remain elevated, suggesting little respite for most currencies against the USD. The recent moves have left net aggregate USD positioning registering an all time high according to the CFTC Commitment of Traders data, in the latest week, but after the slight retracement lower in the USD index, it is set to make further gains over coming days.
It was notable that EUR and GBP looked more composed at the tail end of the week whilst attention turned to the liquidation of long positions in CHF, AUD, NOK and SEK. These risk currencies are set to remain under pressure but there will be little respite for EUR which is set to drift lower, albeit a less aggressive pace than over recent weeks and a re-test of EUR/USD technical support around 1.2296 is likely. GBP/USD has showed some resilience over recent days but remains vulnerable to further downside pressure, with 1.4310 immediate support.