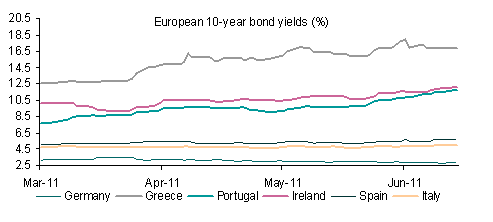
EUR and risk currencies in general were buoyed by the passage of the austerity bill in the Greek parliament. The implementation bill is also likely to be passed later today opening the door for the disbursement of EUR 12 billion from the European Union / IMF from the EUR 110 bailout agreed for the country. Combined with news that German banks are progressing towards agreeing on a mechanism to roll over Greek debt alongside French banks as well as likelihood of an European Central Bank (ECB) rate hike next week, the EUR is set to remain supported over the short term.
Nonetheless, it once again looks as though a lot of good news is priced in and it would be surprising if EUR/USD could extend to above strong resistance around 1.4557 given the many uncertainties ahead, not the least of which includes the stance of ratings agencies on any Greek debt rollover.
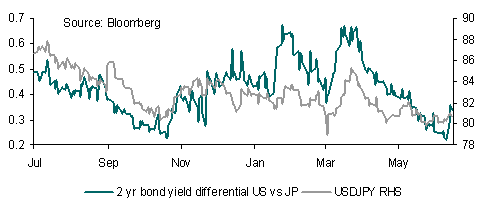
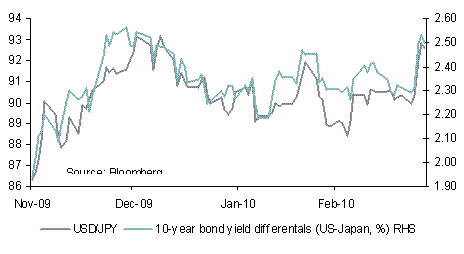
USD/JPY is the only major currency pair that is correlated with bond yield differentials at present (2-year yields) and therefore it should not come as a surprise that USD/JPY has moved higher as the yield differential between the US and Japan has widened by around 10bps over the past week. Indeed, yesterday’s move above 81.00 was spurred by the move in yield differentials although once again the currency pair failed to build sufficient momentum to close above this level.
Further gains will require US bond yields to move even higher relative to Japan but perhaps the end of QE2 today may mark a turning point for US bond markets and currencies. The end of QE2 taken together with a jump in bond supply over coming months, will see US Treasury yields will move sharply higher, implying much more upside for USD/JPY.
AUD has bounced back smartly over recent days, with the currency eyeing resistance around 1.0775 versus USD. A general improvement in risk appetite has given the currency some support but markets will be unwilling to push the currency much higher ahead of the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) meeting next week. On the plus side, there are no rate hikes priced in for Australia over the remainder of the year, suggesting an asymmetric risk to next week’s meeting.
In other words, unless the RBA openly discusses rate cuts in the statement, the AUD will likely remain supported. Conversely any indication that a rate hike may be in prospect will be AUD supportive. In any case we continue to believe the AUD offers better value especially relative to NZD and maintain our trade idea to buy AUD/NZD.