The USD succumbed to further pressure overnight as Moody’s Investor Service threatened to place the US Aaa rating on review for downgrade if there is no agreement reached on raising the US debt ceiling. Although the news prompted a rise in US Treasury yields it did little for the USD.
News that the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet expanded to a record $2.772 trillion in the week ending June 1 highlights the ongoing headwinds to the USD from Fed asset purchases. The fact that there is even talk of QE3 in the wake of weak US data suggests that the headwinds will not dissipate quickly.
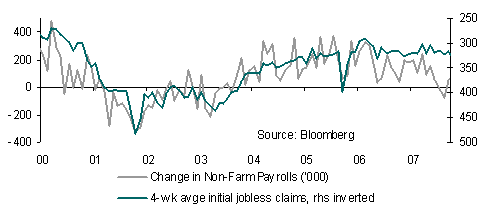
Direction today will come from the US May jobs report though this is unlikely to deliver any good news for the USD. Forecasts for non-farm payrolls have likely been revised lower to sub 100k compared to the published consensus forecast of 165k following the weaker indications from the May ADP jobs report and ISM data this week. A weak payrolls outcome will only intensify worries about the depth and length of the US ‘soft patch’.
Although market expectations are also likely to have been downwardly revised, something that may cushion the blow to the USD, it will be difficult to get away from the fact that growth in Q2 is weaker than many had thought.
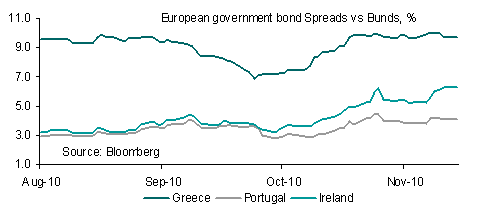
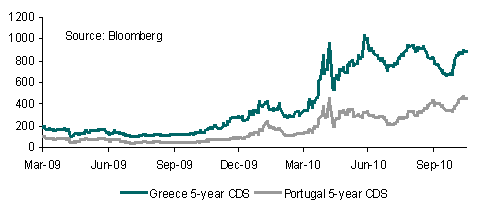
EUR was well supported overnight, boosted by a relatively successful Spanish bond auction yesterday and reports that officials have agreed in principle to a 3-year adjustment plan for Greece covering funding needs to 2013 although there was no confirmation of such an agreement.
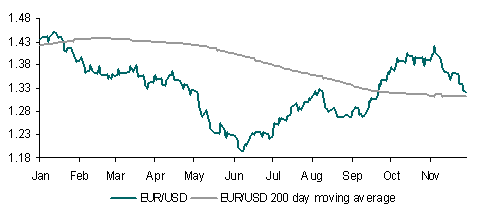
As a result, EUR/USD tested 1.45 and looks supported ahead of today’s US payrolls data. EUR’s recovery in general has been impressive but gains above 1.45 are likely to prove more difficult even if an agreement on Greece is close to being achieved.
As usual Japan’s political gyrations are having little impact on the JPY as the currency is instead buffeted by risk aversion swings and yield differentials. In fact USD/JPY has been rather well behaved over recent weeks as indicated by implied options volatility.
Prime Minister Kan’s success in winning a no-confidence motion came at a cost and may provide very little political stability. Kan said will resign as soon as post-earthquake recovery efforts are completed and once he is gone there is likely to be some realignment of existing political parties.
As for the JPY it will remain unscathed by political events. Over the near term USD/JPY is likely to cling to the 81 handle but we maintain our bearish view on the JPY in the medium term under the assumption that there is a sharp widening in US – Japan bond yield differentials.