The G20 meeting of Finance Ministers and Central bankers failed to establish any agreement on clear targets or guidelines. Perhaps the problem of trying to achieve consensus amongst a variety of sometimes conflicting views always pointed to an outcome of watered down compromise but in the event the G20 summit appears to pass the buck to November’s summit of G20 leaders in Seoul where more concrete targets may be outlined.
Officials pledged to “move towards more market determined exchange rate systems” and to “refrain from competitive devaluation of currencies”. What does this actually mean? The answer is not a great deal in terms of practical implications. The first part of the statement is the usual mantra from such meetings and the addition of the latter part will do little to stop central banks, especially in Asia from continuing to intervene given that no central bank is actually devaluing their currency but rather preventing their currencies from strengthening too rapidly.
The communiqué highlighted the need for advanced economies being “vigilant against excess volatility and disorderly movements in exchange rates”, but once again this is the mantra found in the repertoire of central bankers over past years and is unlikely to have the desired effect of reducing the “excessive volatility in capital flows facing some emerging countries”. In other words many emerging countries will continue to have an open door to impose limited restrictions on “hot money” flows.
Although the language on currencies was stronger than in previous summits it arguably changes very little in terms of the behaviour of central banks and governments with respect to currencies. The communiqué is wide open to varying interpretations by countries and is unlikely to prevent the ongoing trend of USD depreciation and emerging market country FX appreciation and interventions from continuing over coming weeks.
The onus has clearly shifted to the November summit of G20 leaders but once again it seems unlikely that substantial agreements will be found. In the interim the November 3 Fed FOMC meeting will be the next major focus and if the Fed embarks on renewed asset purchases as widely expected FX tensions will remain in place for some time yet.
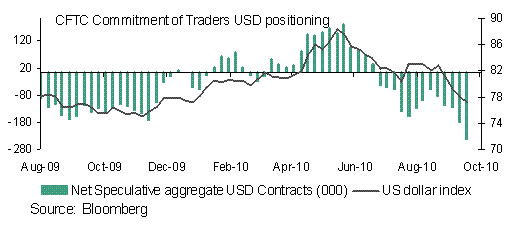
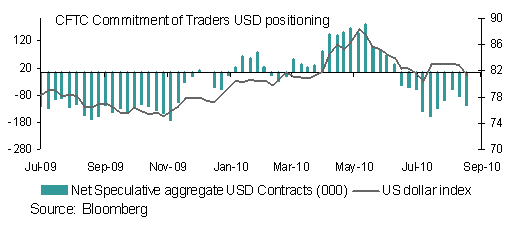
So whilst a “currency war” was always unlikely “skirmishes” will continue. In the meantime the USD is set to remain under pressure although it’s worth noting that speculative positioning has recorded a reduction in net aggregate USD short positions over the last couple of weeks, suggesting that some of the USD selling pressure may have abated. Whether this reflected caution ahead of the G20 meeting (as the data predates the G20 meeting) or indicated the USD having priced in a lot of quantitative easing (QE2) expectations already, is debatable.
The path of least resistance to USD weakness remains via major currencies including AUD, CAD and NZD. Officials in Europe are also showing little resistance to EUR strength despite the premature tightening in financial conditions and negative impact on growth that it entails. Scandinavian currencies such as SEK and NOK have also posted strong gains against the USD and will likely continue to show further outperformance.
The JPY has been the best performing major currency this year followed not far behind by the CHF despite the FX interventions of the authorities in Japan and Switzerland. Although USD/JPY is fast approaching the 80.00 line in the sand level expected to result in fresh FX intervention by the Japanese authorities, the path of the JPY remains upwards. Japan is unlikely to go away from the G20 meeting with any change in policy path as indicated by officials following the weekend deliberations.