A confluence of factors have come together to sour market sentiment although there appeared to be some relief, with a soft US inflation reading (core CPI now at 0.6% YoY) and plunge in US October housing starts reinforcing the view that the Fed will remain committed to carry out its full QE2 program, if not more.
However any market relief looks tenuous. Commodity prices remain weak, with the CRB commodities index down 7.4% in just over a week whilst the Baltic Dry Index (a pretty good forward indicator of activity and sentiment) continues to drop, down around 21% since its recent high on 27 October. Moreover, oil prices are also sharply lower. Increasingly the drop in risk assets is taking on the form of a rout and many who were looking for the rally to be sustained into year end are getting their fingers burnt.
Worries about eurozone peripheral countries debt problems remains the main cause of market angst, with plenty of attention on whether Ireland accepts a bailout rumoured to be up EUR 100 billion. Unfortunately Ireland’s reluctance to accept assistance has turned into a wider problem across the eurozone with debt in Portugal, Greece and also Spain suffering. An Irish bailout increasingly has the sense of inevitability about it. When it happens it may offer some short term relief to eurozone markets but Ireland will hardly be inspired by the fact that Greece’s bailout has had little sustainable impact on its debt markets.
Ireland remains the primary focus with discussions being enlarged to include the IMF a well as ECB and EU. What appears to be becoming clearer is that any agreement is likely to involve some form of bank restructuring, with the IMF likely to go over bank’s books during its visit. Irish banks have increasingly relied on ECB funding and a bailout would help reduce this reliance. Notably the UK which didn’t contribute to Greece’s aid package has said that it will back support for Ireland, a likely reaction to potential spillover to UK banks should the Irish situation spiral out of control. Any bailout will likely arrive quite quickly once agreed.
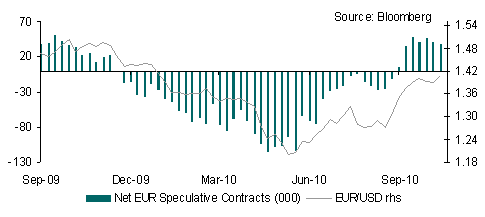
Although accepting a bailout may give Ireland some breathing room its and other peripheral county problems will be far from over. Uncertainties about the cost of recapitalising Ireland’s bank will remain whilst there remains no guarantee that the country’s budget on December 7 (or earlier if speculation proves correct) will be passed. Should Ireland agree to a bailout if may provide the EUR will some temporary relief but FX markets are likely to battle between attention on Fed QE2 and renewed concerns about the eurozone periphery, suggesting some volatile price action in the days and weeks ahead.
Reports of food price controls of and other measures to limit hot money inflows into China as well as prospects for further Chinese monetary tightening, are attacking sentiment from another angle. China’s markets have been hit hard over against the background of such worries, with the Shanghai Composite down around 10% over the past week whilst the impact is also being felt in many China sensitive markets across Asia as well as Australia. For instance the Hang Seng index is down around 7% since its 8 November high.