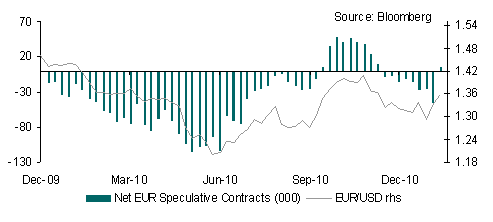
Following a brief rally at the start of the year the USD has found itself under growing pressure in the wake of widening interest rate differentials versus many other currencies. In particular, the contrasting stance between the hawkish rhetoric (bias for tighter monetary conditions) from European Central Bank (ECB) President Trichet and the relatively dovish US Federal Reserve stance as highlighted in the 26th January FOMC statement has provided more fuel to the widening in interest rate expectations between the US and eurozone. Since the end of last year interest rate differentials have widened by around 31 basis points in favour of the EUR (second general interest rate futures contract).
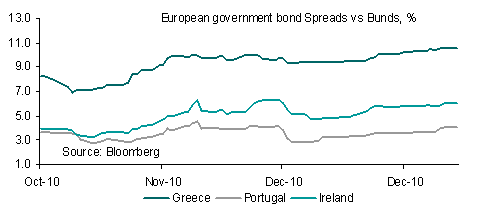
The Fed remains committed to carrying out its full $600 billion of asset purchases by end Q2 2011 whilst the ECB appears to be priming the market for a scaling back of its liquidity operations. Whilst there may be more juice in EUR over the short term based on the move in interest rate differentials as well as improved sentiment towards the eurozone periphery the upside potential for EUR/USD is looking increasingly limited. Even European officials are beginning to inject a dose of caution, with the ECB’s Nowotny stating that markets are too euphoric over a potential enlargement of the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) bailout fund. Indeed, it is highly likely that the euphoria fades quickly once it becomes apparent that enlarging the bailout fund is by no means a panacea to the region’s ailments.
GBP is another currency that has undergone sharp gyrations over recent days in the wake of a shift in interest rate expectations. A surprise 0.5% quarterly drop in UK Q4 GDP (which could not all be blamed on poor weather) set the cat amongst the pigeons and gave a GBP a thrashing but much of this was reversed following the release of Bank of England Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) minutes which revealed a hawkish shift within the MPC, with two dissenters voting for a rate hike and most members agreeing that the risks to inflation has probably shifted higher.
Does this imply an imminent rate hike? No, a policy rate hike closer to the end of the year appears more likely. BoE Governor King provided support to this view, in a speech that was interpreted as dovish, with the governor once again highlighting the temporary nature of the current rise in inflation pressure. Consequently UK interest rate expectations have shifted back and forth over recent days, but still remain wider relative to the US since the start of the year. GBP/USD has of course benefitted, but given worries about growth and the dovish message from King, it is unlikely that rate differentials will widen much further. Consequently GBP/USD is unlikely to make much if any headway above 1.6000.