The sweeping gains for the Republican party in the US mid term elections has sharply changed the political dynamic in the US, with the prospects of further fiscal stimulus looking even slimmer than before although the chances of the Bush tax cuts being extended have likely increased.
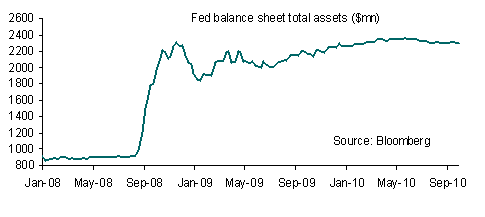
The onus is on monetary policy to do the heavy lifting and the Fed delivered on its end of the bargain, with the announcement of $600 billion of purchases of long-term securities over 8-months through June 2011.
Given the likelihood that the economic impact of the asset purchases is likely to be limited and with little help on the fiscal front the Fed has got a major job on its hands and $600 billion may end up being a minimum amount of purchases necessary for the Fed to fulfil its mandate.
The decline in the USD following the Fed decision is unlikely to mark the beginning of a more rapid pace of USD decline though further weakness over coming months remains likely. The USD remains a sell on rallies for now and an overshoot on the downside is highly probable as the Fed begins its asset purchases.
The bottom line is that the Fed’s program of asset purchases implies more USD supply and in simple economic terms more supply without an increase in demand implies a lower price. The USD will remain weak for some months to come and the Fed’s actions will prevent any USD recovery as the USD solidifies its position as the ultimate funding currency.
Nonetheless, with market positioning close to extreme levels, US bond yields unlikely to drop much further, and the USD already having sold off sharply in anticipation of QE2, (USD index has dropped by around 14% since June) those looking for a further sharp drop in the USD to be sustained are likely to be disappointed.
It is difficult however, to fight the likely further weakness in the USD even if turns out not to be a rapid decline. The path of least resistance to some likely USD weakness will be via the likes of the commodity currencies, scandies and emerging market currencies. There will be less marked appreciation in GBP, CHF and JPY against the USD.
The Fed’s actions will continue to fuel a rush of liquidity into emerging markets, particularly into Asia. This means more upward pressure on Asian currencies but will likely prompt a variety of responses including stronger FX intervention as well as measures to restrict and control such flows.
There have been various comments from central banks in the region warning about the Fed’s actions prompting further “hot money” flows into the region and even talk of a coordinated response to combat such flows.
This suggests more tensions ahead of the upcoming G20 meeting in Seoul. Assuming that at least some part of the additional USD liquidity flows into Asia, the implications of potentially greater FX intervention by Asian central banks to prevent Asian currencies from strengthening, will have a significant impact on major currencies.
Already it is apparent that central banks in Asia have been strongly using the accumulated USDs from FX intervention to diversify into EUR and other currencies including AUD and even JPY. Perversely this could end up exacerbating USD weakness against major currencies.