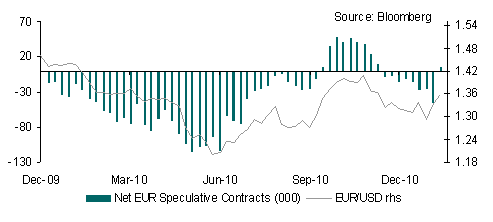
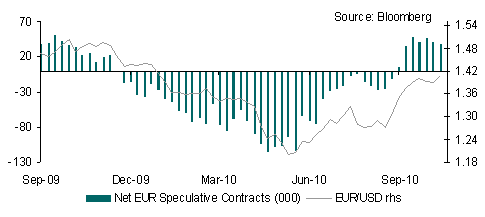
The bounce in the EUR against a broad range of currencies as well as a shift in speculative positioning highlights a sharp improvement in eurozone sentiment. Indeed, the CFTC IMM data reveals that net speculative positioning has turned positive for the first time since mid-November. A rise in the German IFO business confidence survey last week, reasonable success in peripheral bond auctions (albeit at unsustainable yields), hawkish ECB comments and talk of more German support for eurozone peripheral countries, have helped.
A big driver for EUR at present appears to be interest rate differentials. In the wake of recent commentary from Eurozone Central Bank (ECB) President Trichet following the last ECB meeting there has been a sharp move in interest rate differentials between the US and eurozone. This week’s European data releases are unlikely to reverse this move, with firm readings from the flash eurozone country purchasing managers indices (PMI) today and January eurozone economic sentiment gauges expected.
Two big events will dictate US market activity alongside more Q4 earnings reports. President Obama’s State of The Union address is likely to pay particular attention on the US budget outlook. Although the recent fiscal agreement to extend the Bush era tax cuts is positive for the path of the economy this year the lack of a medium to long term solution to an expanding budget deficit could come back to haunt the USD and US bonds.
The Fed FOMC meeting on Wednesday will likely keep markets treading water over the early part of the week. The Fed will maintain its commitment to its $600 billion asset purchase program. Although there is plenty of debate about the effectiveness of QE2 the program is set to be fully implemented by the end of Q2 2011. The FOMC statement will likely note some improvement in the economy whilst retaining a cautious tone. Markets will also be able to gauge the effects of the rotation of FOMC members, with new member Plosser possibly another dissenter.
These events will likely overshadow US data releases including Q4 real GDP, Jan consumer confidence, new home sales, and durable goods orders. GDP is likely to have accelerated in Q4, confidence is set to have improved, but at a low level, housing market activity will remain burdened by high inventories and durable goods orders will be boosted by transport orders. Overall, the encouraging tone of US data will likely continue but markets will also keep one eye on earnings. Unfortunately for the USD, firm US data are being overshadowed by rising inflation concerns elsewhere.
Against the background of intensifying inflation tensions several rate decisions this week will be of interest including the RBNZ in New Zealand, Norges Bank in Norway and the Bank of Japan. All three are likely to keep policy rates on hold. There will also be plenty of attention on the Bank of England (BoE) MPC minutes to determine their reaction to rising inflation pressures, with a slightly more hawkish voting pattern likely as MPC member Posen could have dropped his call for more quantitative easing (QE). There will also be more clues to RBA policy, with the release of Q4 inflation data tomorrow.
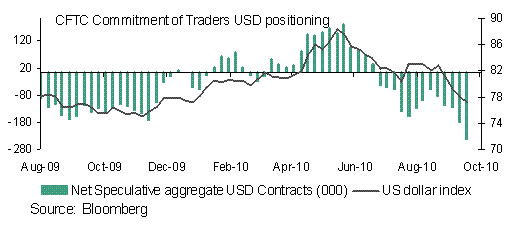
Both the EUR and GBP have benefitted from a widening in interest rate futures differentials. In contrast USD sentiment has clearly deteriorated over recent weeks as highlighted in the shift in IMM positioning, with net short positions increasing sharply. It is difficult to see this trend reversing over the short-term, especially as the Fed will likely maintain its dovish stance at its FOMC meeting this week. This suggests that the USD will remain on the back foot.