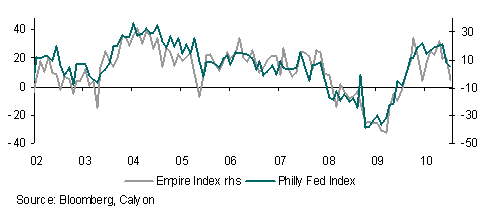
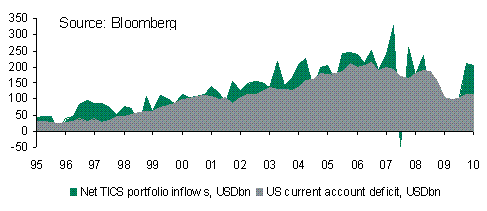
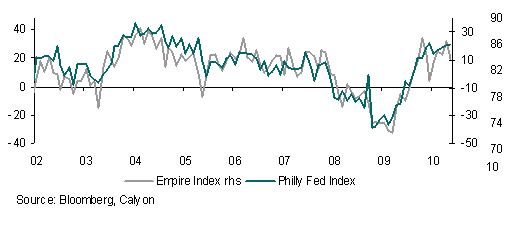
The latest in a long line of disappointing US data was released on Friday. University of Michigan consumer confidence sent an alarming signal about the propensity of the US consumer to contribute to economic recovery. Confidence dropped much more than expected, to its lowest level since August 2009, fuelling yet more angst about a double-dip in growth.
The Fed’s relatively dovish FOMC minutes last week contributed to the malaise and undermined the USD in the process as attention switched from the timing of exit strategies to whether the Fed will expand quantitative easing. Friday’s benign June CPI report left no doubt that the Fed has plenty of room on its hands, with core inflation remaining below 1% and likely to decelerate further over the coming months. Against this background Fed Chairman Bernanke’s semi-annual testimony to the US Congress (Wed/Thu) will be a particular focus, especially if he hints at potential for further QE, a possibility that appears remote, but could harm the USD.
Arguably the biggest event of the week is the European bank stress test results on Friday. Although several European governments have suggested that the banks in their countries will pass the tests there is still a considerable event risk surrounding the announcement. 91 banks are being tested and much will depend on how rigorous the tests are perceived to be. Should they be seen not to be sufficiently thorough, for instance in determining a realistic haircut on sovereign debt holdings, the potential for pressure on the EUR to increase once again will be high. Similarly debt auctions across Europe this week will also garner interest but similar success to last week’s Spanish auction cannot be guaranteed.
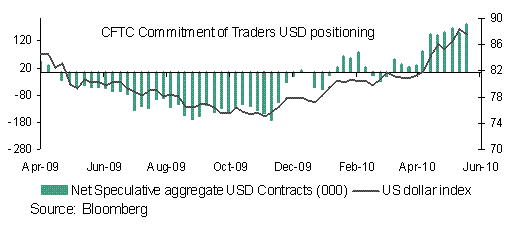
The big question in FX markets is whether the EUR can hold onto its recent gains and whether the USD will be punished further amidst growing double-dip worries. Interestingly the USD’s reaction on Friday to the soft consumer confidence data was not as negative as has been the case recently, with higher risk aversion once again outweighing negative cyclical influences. Various risk currencies actually came under pressure against the USD and this is likely to extend into this week. Despite a threat to the USD from any QE hints by Bernanke, speculative positioning has turned net short USD once again suggesting potential for less USD selling.
The bigger risk this week is to the EUR, which could face pressure on any disappointment from the bank stress test results. The EUR was strong against most major currencies last week, suggesting that the strengthening in EUR/USD is less to do with USD weakness, but more related to EUR strength. This strength in the EUR is hard to tally with the worsening economic outlook in the eurozone and the fact that a stronger EUR from an already overvalued level will crimp eurozone growth further. The latest CFTC IMM data has revealed a further covering of short positions, but this is likely to be close to running its course. Technically EUR/USD has broken above its ‘thick’ Ichimoku cloud, and the weekly MACD is turning above its signal line from oversold levels suggesting a period of further strength but its gains are set to be short-lived.