Most investors will be glad to see the back of August, a month that marked the biggest monthly decline in US stocks in nine years. The main imponderable is whether September will be any better. A series of manufacturing surveys globally today will do little to restore confidence although there was some good news in a slight increase in China’s official August purchasing managers index (PMI) as well a stronger than forecast increase in Australian Q2 GDP, which will likely provide some short-term relief for risk trades.
There was also some slight solace for markets in terms of US data at least from the point of view that the data was not as disappointing as many recent releases. Although the August Chicago PMI slipped (to 56.7) consumer confidence increased (to 53.5) though admittedly confidence remains at a relatively low level. The job market situation detailed within the consumer confidence report was more pessimistic in August than the previous month, however, with those reporting jobs hard to get moving higher. This sends a negative signal for Friday’s payrolls data.
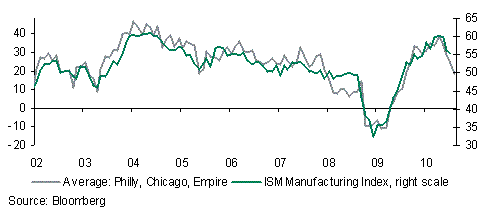
There will be more clues to Friday’s US jobs report today which will enable any fine tuning of forecasts to take place in the wake of the August ADP employment report and ISM manufacturing survey. Consensus forecasts centre on a 15k increase in private jobs. Despite the slight increase in the Empire manufacturing survey in August, the falls in other manufacturing surveys point to some downside risks to the ISM today, with a simple average of the three pointing to the ISM closer to the 50 mark, which will highlight a loss in US manufacturing momentum.
Manufacturing surveys elsewhere will also be in focus, with the final PMI readings scheduled to be released for the eurozone and UK. There is likely to be confirmation of the slight drop in the eurozone PMI to 55.0 in August while the UK PMI is likely to drop to around 57.0 over the month. Both surveys remain at a relatively high level but it is clear that activity is moderating in H2 2010 from a healthy level in H2. The data will give little support to the EUR but the currency has found a degree of stability over the last couple of days. Nonetheless, a further downward move is in prospect.
The Fed FOMC minutes provided little for markets to get excited about. The minutes noted concerns about large scale asset purchases from some Fed officials, indicating resilience to increasing quantitative easing despite acknowledging increased downside risks to the growth and inflation outlook. It is unclear exactly what will be the trigger for further QE as acknowledged by Fed Chairman Bernanke last week.
The minutes will do little to help market confidence given the hesitancy to pursue further QE and provide further stimulus to the economy but the USD is likely to benefit from the fact that the Fed may not be as eager to expand its balance sheet further. Other currencies that remain beneficiaries in the current risk averse environment are the JPY and CHF. The JPY may find further upside more difficult given ongoing intervention fears but the trend remains for a lower USD/JPY in the coming weeks.