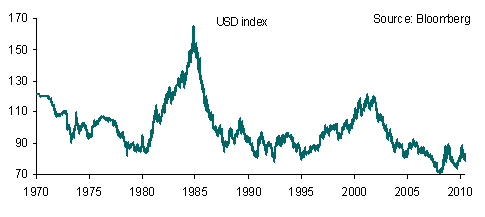An encouraging run of US data releases over recent weeks became even more solid overnight. In particular the December ADP private sector jobs report revealed a whopping 297k increase, its highest ever reading. Although the outsized gain may be attributable to distortions such as seasonal factors it will lead many to scramble to revise higher estimates for non-farm payrolls to around 200k+ (consensus currently is 150k). Similarly the December ISM non-manufacturing survey came in higher than expected at 57.1, its highest reading since May 2006. Notably the employment component softened in contrast to the ADP data.
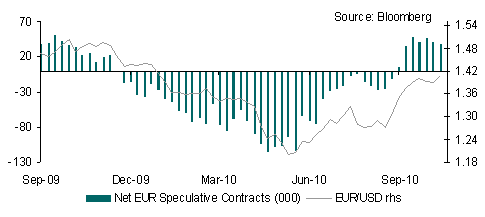
Whilst the US outlook appears to be improving the eurozone picture is looking decidedly shaky. Peripheral bonds remain under pressure as reflected in the renewed widening in German-Greek spreads whilst Portugal’s sale of 6m bills revealed good demand but at a much higher yield (3.69% vs. 2.05% in September). Press reports that the Swiss National Bank has stopped accepting Irish government debt as collateral didn’t help matters whilst talk of conditions attached to any Chinese support for eurozone countries also weighed on sentiment.
Adding to concerns is the ongoing political impasse in Belgium where 7 months after elections there has yet to be a new government formed. The risk of a downgrade to the country’s credit ratings is high especially given the lack of progress on deficit reduction. Meanwhile on the data front the Eurozone service sector PMI was stronger than forecast in December at 54.2 but the country breakdown revealed more divergence in economic conditions. This was echoed in the manufacturing PMI. Divergence in growth is likely to widen further this year and whilst the strength of Germany may prevent a sharp slowing in overall growth in the eurozone, growing divergence will make the job of the ECB difficult.
The net result of firmer US data is a broadly stronger USD and higher Treasury yields. The EUR in contrast looks as though it is on the verge of a sharper decline below 1.3000, with technical support seen around 1.2969 whilst the JPY could see further weakness given the move in relative US/Japan bond yields. There will be little direction today from data with just Eurozone sentiment gauges and retail sales tap whilst in the US jobless claims will be in focus. However, there will probably be little movement ahead of the US jobs report tomorrow.