At the end of a momentous week for currency markets it’s worth taking stock of how things stand. Much uncertainty remains about the global growth outlook, especially with regard to the US economy, potential for a double-dip and further Fed quantitative easing. Although there is little chance of QE2 being implemented at next week’s Fed FOMC meeting speculation will likely remain rife until there is clearer direction about the path of the US economy.
In Europe, sovereign debt concerns have eased as reflected in the positive reception to debt auctions this week. Nonetheless, after a strong H1 2010 in terms of eurozone economic growth the outlook over the rest of the year is clouded. Such uncertainty means that markets will also find it difficult to find a clear direction leaving asset markets at the whim of day to day data releases and official comments.
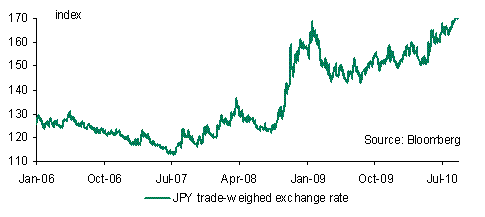
The added element of uncertainty has been provided by Japan following its FX intervention this week. Whilst Japanese officials continue to threaten more intervention this will not only keep the JPY on the back foot but will provide a much needed prop for the USD in general. Indeed Japan’s intervention has had the inadvertent effect of slowing but not quite stopping the decline in the USD, at least for the present.
The fact that Japanese officials continue to threaten more intervention suggests that markets will be wary of selling the USD aggressively in the short term. The headwinds on the USD are likely to persist for sometime however, regardless of intervention by Japan and/or other Asian central banks across Asia, until the uncertainty over the economy and QE2 clears.
Japan’s intervention has not gone down well with the US or European authorities judging by comments made by various officials. In particular, the FX intervention comes at a rather sensitive time just as the US is piling on pressure on China to allow its currency the CNY to strengthen further. Although US Treasury Secretary Geithner didn’t go as far as proposing trade and legal measures in his appearance before Congress yesterday there is plenty of pressure from US lawmakers for the administration to take a more aggressive stance, especially ahead of mid-term Congressional elections in November. Ironically, the pressure has intensified just as China has allowed a more rapid pace of CNY nominal appreciation over recent days although it is still weaker against its basket according to our calculations.
Another country that has seen its central bank intervening over many months is Switzerland, with the SNB having been aggressively intervening to prevent the CHF climbing too rapidly. However, in contrast to Japan the SNB is gradually stepping back from its intervention policy stating yesterday that it would only intervene if the risk of deflation increased. Even so, Japan may have lent the Swiss authorities a hand, with EUR/CHF climbing over recent days following Japan’s intervention.
The move in EUR/CHF accelerated following yesterday’s SNB policy meeting in which the Bank cut its inflation forecasts through 2013, whilst stating that the current policy stance in “appropriate”. Moreover, forecasts of “marked” slowdown in growth over the rest of the year highlight the now slim chance of policy rates rising anytime soon. Markets will eye technical resistance around 1.3459 as a near term target but eventually the CHF will likely resume its appreciation trend, with a move back below EUR/CHF 1.3000 on the cards.