In an otherwise unexciting day China livened things up by raising its 1 year deposit and lending rates by 25 basis points. The hike, the third in the last four months, should not have come as a surprise, given the growing emphasis by China’s central bank PBoC, to dampen inflation pressures. Indeed, more hikes are on the cards, with at least another two more in prospect over H1. The other tool to combat inflation is CNY appreciation further gains in the currency over coming months should be expected to around 6.3 by year-end versus USD.
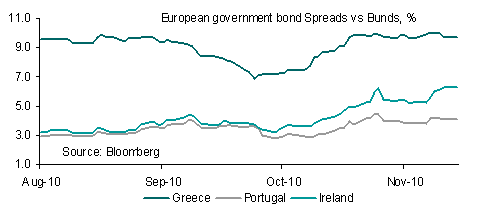
Global markets largely shrugged of China’s move, with generally positive market sentiment continuing. Even in the eurozone, where there was some disappointment at the surprise drop in German December industrial production, market sentiment continued to improve as Egypt and local debt worries eased further. EUR was particularly resilient despite calls from a Belgian think tank that Greece needs to restructure its debt to avoid a long and painful path ahead. Commodity currencies also showed impressive resilience to China’s rate hike, with both the AUD and NZD holding up well.
The overall positive risk background is supportive for Asian currencies and other risk trades. Currencies in Asia remain highly correlated with portfolio capital inflows and so far this year the weakness in the INR and THB has matched the strong equity outflows from India and Thailand. However, this appears to be reversing, especially in the case of India registering positive equity flows this month, helping the INR to reverse some of its losses.
In the absence of key data releases markets will turn their attention to the testimony by Fed Chairman Bernanke to the House budget committee where he will give comments on the economy, jobs and the budget. Dallas Fed’s Fisher stated overnight that whilst he expects the Fed to complete QE2 he would not support another round of quantitative easing. Fisher’s comments on QE were similar to Atlanta Fed’s Lockhart who notes there is a “high bar” for more QE. Bernanke is unlikely to deviate from this tone in his speech today whilst also maintaining his view that there should be a long term commitment to fiscal retrenchment.
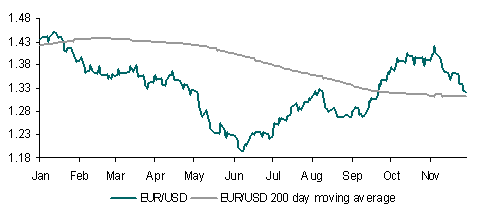
Against the background of improving risk appetite the USD is likely to stay under mild pressure although it is difficult to see a break of recent ranges for most currency pairs. EUR/USD ought to find strong support around its 100-day moving average 1.3535 whilst USD/JPY will be supported around 81.10. Equity sentiment is being supported by US data which remains encouraging. On cue the NFIB Small Business Optimism index duly rose in January to 94.1 as sentiment in this sector continued its improving trend.
Taken together with firmer equities, encouraging data is taking its toll on US bond markets, resulting in a back up in yields. Bond market sentiment wasn’t helped by a relatively poor 3-year auction. For example, US 2-year bond yields have backed up by over 30bps since 28 January. Bad news for bond is good news for the USD however, as higher relative US bond yields will likely help prevent a deeper USD sell-off, with EUR/USD in particular most reactive to relative eurozone / US bond yield differentials.
Econometer.org has been nominated in FXstreet.com’s Forex Best Awards 2011 in the “Best Fundamental Analysis” category. The survey is available at http://www.surveymonkey.com/s/fx_awards_2011