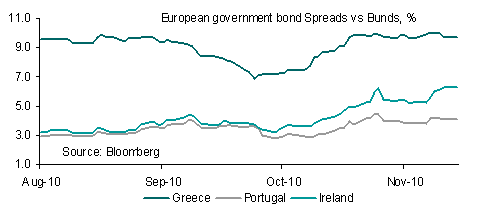
As has been the case since the beginning of the global financial crisis policy makers have found themselves under pressure to deliver a solution to a potentially destabilising or even systemic risk before the markets open for a new week in order to prevent wider contagion. Last night was no different and following urgent discussions a EUR 85 billion bailout for Ireland to be drawn down over a period of 7 ½ years was agreed whilst moves towards a permanent crisis mechanism were brought forward. As was evident over a week ago a bailout was inevitable but the terms were the main imponderable.
Importantly the financing rate for the package is lower than feared (speculation centered on a rate of 6.7%) but still relatively high at 5.8%. Moreover, no haircuts are required for holders of senior debt of Irish banks and Germany’s call for bondholders to bear the brunt of losses in future crises was watered down. The package will be composed of EUR 45 bn from European governments, EUR 22.5 bn from the IMF and EUR 17.5 bn from Ireland’s cash reserve and national pension fund.
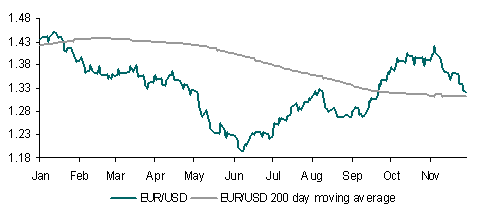
The impact on the EUR was stark, with the currency swinging in a 120 point range and failing to hold its initial rally following the announcement. A break below the 200-day moving average for EUR/USD around 1.3131 will trigger a drop to around 1.3020 technical support. Officials will hope that the bailout offers the currency some deeper support but this already seems to be wishful thinking. The EUR reaction following the Greek bailout in early May does not offer an encouraging comparison; after an initial rally the EUR lost close to 10% of its value over the following few weeks.
Although it should be noted that the bailout appears more generous than initially expected clearly the lack of follow through in terms of EUR upside will come as a blow. The aid package has bought Ireland some breathing space but this could be short lived if Ireland’s budget on December 7 is not passed. Moreover, the bailout will not quell expectations that Portugal and perhaps even Spain will require assistance. Indeed, Portugal is the next focus and the reaction to an auction of 12-month bills on 1 December will be of particular interest.
Taken together with continued tensions on the Korean peninsular, position closing towards year end ongoing Eurozone concerns will likely see a further withdrawal from risk trades over coming weeks. For Asian currencies this spells more weakness and similarly commodity currencies such as AUD and NZD also are likely to face more pressure. The USD remains a net beneficiary even as the Fed continues to print more USDs in the form of QE2.
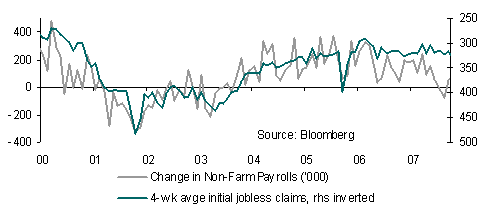
Data and events this week have the potential to change the markets perspective, especially the US November jobs report at the end of the week. There is no doubt that payrolls are on an improving trend (145k consensus) in line with the declining trend in jobless claims but unfortunately the unemployment rate is set to remain stubbornly high at 9.6% and this will be the bigger focus for the Fed and markets as it implies not let up in QE. As usual further clues to the payrolls will be garnered from the ADP jobs report and ISM data on Wednesday.