Pressure, panic and carnage doesn’t even begin to describe the volatility and movements in markets last week. If worries about global economic growth and the eurozone debt crisis were not enough to roil markets the downgrade of the US sovereign credit rating after the market close on Friday sets the background for a very shaky coming few days. All of this at a time when many top policy makers are on holiday and market liquidity has thinned over the summer holiday period.
The downgrade of US credit ratings from the top AAA rating should not be entirely surprising. After all, S&P have warned of a possible downgrade for months and the smaller than hoped for $2.1 trillion planned cuts in the US fiscal deficit effectively opened the door for a ratings downgrade. Some solace will come from the fact that the other two main ratings agencies Moody’s and Fitch have so far maintained the top tier rating for the US although Fitch will make it’s decision by the end of the month.
Comparisons to 2008 are being made but there is a clear difference time this time around. While in 2008 policy makers were able to switch on the monetary and fiscal taps the ammunition has all but finished. The room for more government spending in western economies has now been totally used up while interest rates are already at rock bottom. Admittedly the US Federal Reserve could embark on another round of asset purchases but the efficacy of more quantitative easing is arguably very limited.
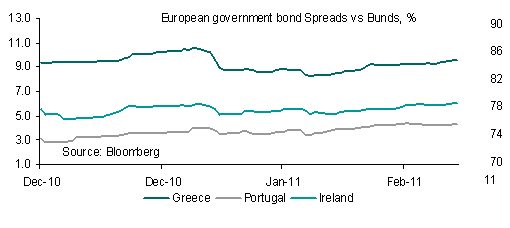
Confidence is shattered so what can be done to turn things around? European policy makers had hoped that their agreement to provide a second bailout for Greece and beef up the EFSF bailout fund would have stemmed the bleeding but given the failure to prevent the spreading of contagion to Italy and Spain it is difficult to see what else they can do to stem the crisis.
Current attempts can be likened to sticking a plaster on a grevious wound. Although I still do not believe that the eurozone will fall apart (more for political rather than economic reasons) eventually there may have to be sizeable fiscal transfers from the richer countries to the more highly indebted eurozone countries otherwise the whole of the region will be dragged even further down.
Where does this leave FX markets? The USD will probably take a hit on the US credit ratings downgrade but I suspect that risk aversion will play a strong counter-balancing role, limiting any USD fallout. I also don’t believe that there will be a major impact on US Treasury yields which if anything may drop further given growth worries and elevated risk aversion. It is difficult for EUR to take advantage of the USDs woes given that it has its own problems to deal with.
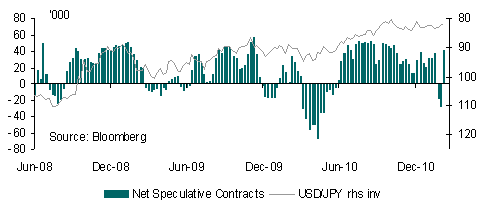
Despite last week’s actions by the Swiss and Japanese authorities to weaken their respective currencies, CHF and JPY will remain in strong demand. Any attempt to weaken these currencies is doomed to failure at a time when risk aversion remains highly elevated, a factor that is highly supportive for such safe haven currencies. From a medium term perspective both currencies are a sell but I wouldn’t initiate short positions just yet.