There has been a sense of mean reversion in FX markets so far this year as some of last year’s winners have become losers. Namely NZD, CHF, JPY and AUD have all lost ground whilst EUR and GBP have gained ground. The odd one out is the SEK which has strengthened over 2010 and in 2011 versus USD. I expect this pattern to change and the likely winners over the next 3- months are NZD, AUD and CAD, with CHF and JPY the likely losers.
EUR held up reasonably well in the wake of slightly disappointing growth data, with eurozone GDP rising less than expected in Q4, and a smaller than expected gain in the February German ZEW investor confidence survey (economic sentiment component). My sense is that the net long EUR speculative position has already been pared back somewhat over recent days reducing the potential selling pressure on the currency in the near term.
Given that EUR/USD is one of the only major currency pairs being influenced by interest rate differentials, its direction will hinge more on policy expectations but in the near the announcement by the German Finance Minister this morning of a restructuring plan for WestLB may give the currency some support.
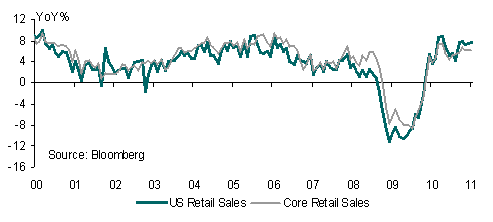
Perhaps one explanation for the stability of EUR/USD around the 1.3500 level is that US data was also disappointing yesterday. January retail sales rose less than forecast whilst revisions to back months suggest less momentum in Q4 consumer spending than previously envisaged. As with the eurozone data weather likely played a role in contributing to the outcome.
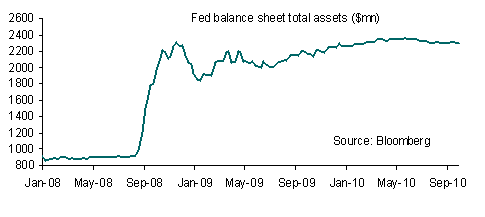
The net impact on currencies is that they are largely stuck within tight ranges. Further direction will come from the release of the Fed FOMC minutes for the January 26th meeting. The minutes may undermine the USD if a likely dovish slant continues to be expressed but given that the FOMC decision at that meeting to hold policy setting unchanged had no dissenters this should not come as a surprise.
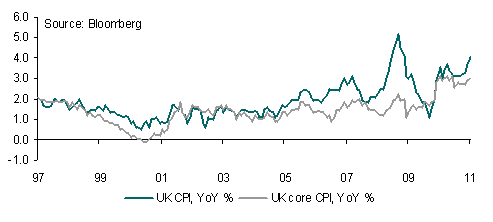
Whilst the battle between the USD and EUR ended in a stalemate GBP outperformed in the wake of the increase in UK January CPI inflation and in particular the letter from the BoE governor to the Chancellor keeping open the door to a rate hike. The Quarterly Inflation Report (QIR) today will be particularly important to determine whether the bounce in GBP is justified.
I remain hesitant to build on long GBP positions given the net long speculative overhang in the currency. The risks following yesterday’s jump in GBP are asymmetric, with a hawkish QIR likely to have less impact on the currency than the negative impact from a more dovish than expected report.
Econometer.org has been nominated in FXstreet.com’s Forex Best Awards 2011 in the “Best Fundamental Analysis” category. The survey is available at http://www.surveymonkey.com/s/fx_awards_2011