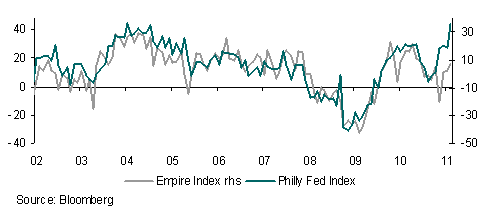
The USD came under pressure despite a higher than forecast reading for January US CPI and a strong jump in the February Philly Fed manufacturing survey. On the flip side, an increase in weekly jobless claims dented sentiment. The overnight rally in US Treasury yields was a factor likely weighing on the USD. The US calendar is light today leaving markets to focus on the G20 meeting and to ponder next week’s releases including durable goods orders, existing and new home sales.
The jump in the European Central Bank (ECB) marginal facility borrowing to EUR 15 billion, its highest since June 2009, provoked some jitters about potential problems in one or more eurozone banks. At a time when there are already plenty of nerves surrounding the fate of WestLB and news that Moody’s is reviewing another German bank for possible downgrade, this adds to an already nervous environment for the EUR.
Nonetheless, EUR/USD appears to be fighting off such concerns, with strong buying interest on dips around 1.3550. The G20 meeting under France’s presidency is unlikely to have any direct impact on the EUR or other currencies for that matter, with a G20 source stating that the usual statement about “excess volatility and disorderly movements in FX” will be omitted.
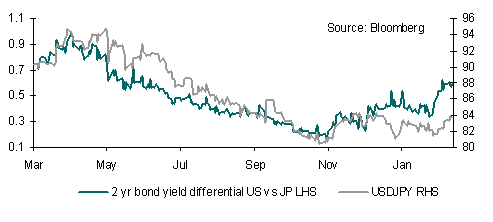
Although USD/JPY has been a highly sensitive currency pair to differentials between 2-year US and Japanese bonds (JGBs), this sensitivity has all but collapsed over recent weeks. USD/JPY failed to break the 84.00 level, coming close this week. There appears to be little scope to break the current range ahead of next week’s trade data and CPI.
Given the recent loss in momentum of Japan’s exports the data will be instructive on how damaging the strength of the JPY on the economy. In the near term, escalating tensions in the Middle East will likely keep the JPY supported, with support around USD/JPY 83.09 on the cards.
It seems that the jump in UK CPI this week (to 4.0%) provoked even more hawkish comments than usual from the Bank of England BoE’s Sentance, with the MPC member stating that the Quarterly Inflation Report understates the upside risks to inflation indicating that interest rates need to rise more quickly and by more than expected. Specifically on GBP he warned that the Bank should not be relaxed about its value.
Although these comments should not be particularly surprising from a known hawk, they may just help to underpin GBP ahead of the January retail sales report. Expectations for a rebound in sales following a weather related drop in the previous month will likely help prop up GBP, with GBP/USD resistance seen around 1.6279.