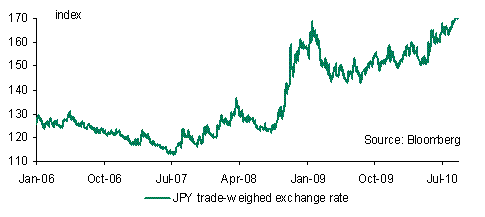
The Bank of Japan acting on the behest of the Ministry of Finance intervened to weaken the JPY, the first such action since 2004. The intervention came as the USD was under broad based pressure, with the USD index dropping below its 200-day moving average. USD/JPY dropped to a low of around 82.88 before Japan intervened to weaken the JPY. The move follows weeks of verbal intervention by the Japanese authorities and came on the heels of the DPJ leadership election in which Prime Minister Kan retained his leadership.
One thing is for certain that Japanese exporters had become increasingly concerned, pained and vocal about JPY strength at a time when export momentum was waning. However, the move in USD/JPY may simply provide many local corporates with better levels to hedge their exposures.
Time will tell whether the intervention succeeds in engineering a sustainable weakening in the JPY but more likely it will only result in smoothing the drop in USD/JPY over coming months along the lines of what has happened with the SNB interventions in EUR/CHF. As many central banks have seen in the past successful intervention is usually helped if the market is turning and in this case USD/JPY remains on a downward trajectory.
Although the BoJ Governor Shirakawa said that the action should “contribute to a stable foreign exchange-rate formation” it is far from clear that the BoJ favoured FX intervention. Indeed, the view from the BoJ is that the move in USD/JPY is related less to Japanese fundamentals but more to US problems.
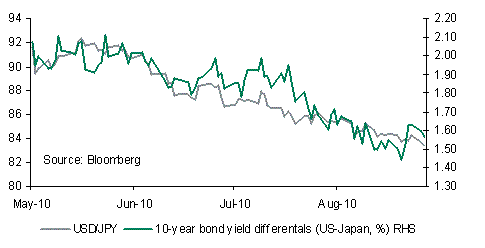
Now that the door is open, further intervention is likely over coming days and weeks but for it to be effective it will require 1) doubts about US growth to recede, 2) speculation of Fed QE 2 to dissipate, 3) and consequently interest rate differentials, in particular bond yields between the US and Japan to widen in favour of the USD. This is unlikely to happen quickly, especially given continued speculation of further US quantitative easing. A final prerequisite to a higher USD/JPY which is related to the easing of some of the above concerns is for there to be an improvement in risk appetite as any increase in risk aversion continues to result in JPY buying.
When viewed from the perspective of Asian currencies the Japanese intervention has put Japan in line with other Asian central banks which have been intervening to weaken their currencies. However, Asian central bank intervention has merely slowed the appreciation in regional currencies, and Japan may have to be satisfied with a similar result. Japan’s intervention may however, give impetus to Asian central banks to intervene more aggressively but the result will be the same, i.e. slowing rather then stemming appreciation.
As for the JPY a further strengthening, with a move to around 80.00 is likely by year end despite the more aggressive intervention stance. Over the short term there will at least be much greater two-way risk, which will keep market nervous, especially if as is likely Japan follows up with further interventions. USD/JPY could test resistance around 85.23, and then 85.92 soon but eventually markets may call Japan’s bluff and the intervention may just end up putting a red flag in front of currency markets to challenge.