The aftermath of the devastating earthquake and Tsunami in Japan will largely drive markets this week outweighing the ongoing tensions in the Middle East. Having been in Tokyo as the earthquake struck I can testify to the severity and shock impact of the earthquake. Aside from the terrible human cost the economic cost will be severe at least for the next few months before reconstruction efforts boost growth. An early estimate suggests around a 1% negative impact on GDP this year.
The government is expected to announce a spending package over coming weeks to help fund relief efforts but this will likely put additional strain on Japan’s precarious debt situation at a time when worries about the country’s fiscal health were already high. Nonetheless, there is around JPY 550 billion available from the Fiscal Year 2010 and FY 2011 budgets even before a supplementary budget is needed.
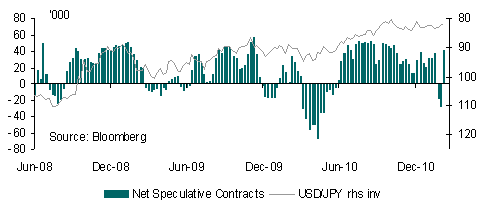
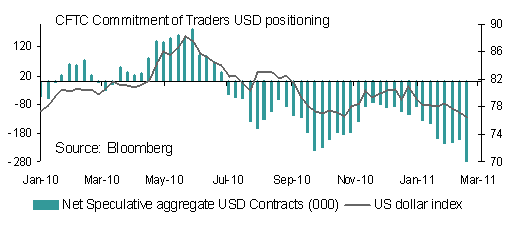
The initial negative JPY impact of the natural disaster gave way to strength in anticipation of expected repatriation flows by Japanese life insurance companies and other institutions as they liquidate assets abroad in order to pay for insurance payments in Japan. The bias to the JPY will likely continue to be upwards but trading will be choppy.
Many of the margin traders holding extreme long USD/JPY positions will likely reduce these positions in the weeks following the earthquake in order to fulfil JPY demand. This may be countered by some foreign selling of Japanese assets especially given that foreigners have accelerated Japanese asset purchases over recent weeks. Therefore, it’s not a straight forward bet to look for JPY strength.
If however, the JPY strengthens rapidly and threatens to drop well below the psychologically important level of 80 the spectre of FX intervention will loom large. Indeed, following the Kobe earthquake in 1995 the JPY strengthened sharply by around 18% but the USD was already in decline prior to the earthquake and USD/JPY was also being pressured lower by Barings Bank related liquidation.
Therefore, comparisons to 1995 should be taken with a pinch of salt. Nonetheless, Japanese authorities will be on guard for further upward JPY pressure. The immediate market focus will be on the Bank of Japan (BoJ) meeting today, with the BoJ announcing the addition of JPY 7 trillion in emergency liquidity support to help stabilise markets.