EUR/USD has rallied over recent days from a low around 1.3146 last week. Market hopes of a eurozone solution may fall flat but the pressure on officials has ratcheted higher, and the risks of failure are now too significant to jeopardize with half measures. Weekend promises of banking sector recapitalisation by Germany and France have helped but will not be enough should such promises prove empty. Markets will likely give the benefit of the doubt to eurozone officials ahead of the delayed October 23 EU Summit and the November 3 G20 meeting.
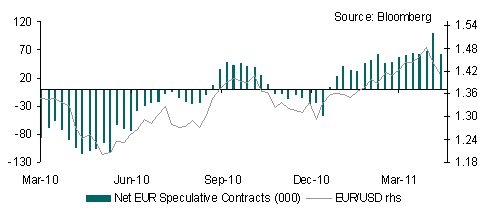
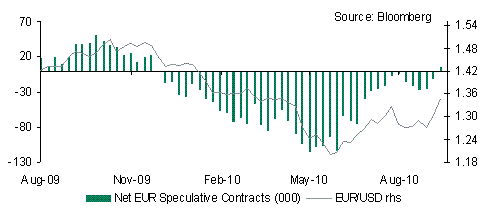
Consequently EUR will find some support over coming days and could extend gains as risk appetite improves; having broken above 1.3600 the next big resistance level for EUR/USD is 1.3800. The fact that EUR speculative positioning is very negative (biggest short position since June 2010 according to IMM data) highlights the potential for short covering.
Possible good news in Greece, with an announcement by the Troika (ECB, EU and IMF) on talks over the next tranche of the bailout will likely provide more EUR support. One stumbling block for the EUR could come from the Slovakian vote on EFSF bailout fund enhancement, which is by no means guaranteed to pass.
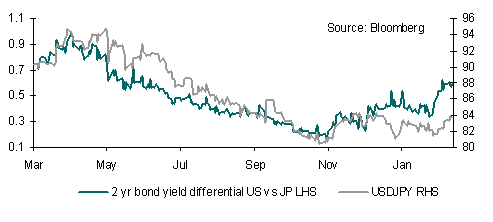
The JPY remains firm benefitting from higher risk aversion, registering one of the highest correlations with risk over recent months. However, the reason why the JPY is not even stronger is that bond yield differentials (especially 2-year) with the US have widened out in favour of the USD over recent days. If the recent improvement in risk appetite continues, combined with widening yield differentials it could push USD/JPY to finally move higher and sustain a break above 77.00.
GBP/USD has made an impressive bounce over recent days from a low around 1.5272 last week despite the Bank of England’s announcement of more quantitative easing last week and credit ratings downgrades of several UK banks. This resilience is impressive but it appears that GBP is caching onto the coat tails of a firmer EUR rather than benefitting from a domestically led improvement in sentiment. Nonetheless, there is scope for further gains in GBP given that speculative positioning in the currency moved close to its all time low early last week in anticipation of BoE QE.